By Jessica Weiss ’05
As an Indian American, Joshua John has long sought to know more about other South Asian figures in U.S. history and politics. So John, a rising junior and double major in economics and Politics, Philosophy and Economics (PPE), decided to focus a research project this summer on former U.S. Representative Dalip Singh Saund, the first-ever Indian American in Congress.
John scoured the archives of the Congressional Record to locate a 1957 speech given by Saund on the House floor advocating for passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1957. In it, Saund cited his own experience as an immigrant as he underscored the absurdity of denying Black Americans voting rights.
John is now preparing an entry about that speech to appear on the website of the “Recovering Democracy Archives” (RDA), a project sponsored by the Rosenker Center for Political Communication & Civic Leadership in the Department of Communication that seeks to create a digital archive of lesser-known but important public speeches throughout U.S. history. The entry will include the transcribed and authenticated speech, a heavily researched “contextualization” paper, photos and more.

John was among the researchers in the seven-week residential Big Ten Academic Alliance Summer Research Opportunities Program (SROP), which seeks to increase the number of underrepresented students who pursue graduate study and research careers through intensive research experiences with faculty mentors and enrichment activities. A total of 10 undergraduates from across the country took part in the SROP at ARHU—three participated in the RDA project, while seven worked on “Enslaved: Peoples of the Historic Slave Trade,” a database containing records on hundreds of thousands of individuals living in the era of the historical slave trade, led in part by UMD researchers.
“This has been an incredible opportunity,” John said. “Learning to do historical research, making a strong historical argument with clear writing—these are new challenges that I have not approached in my academic experience until now and I can feel myself growing through this experience.”
After locating Saund’s speech, John accessed dozens of books, archival and historical documents, political records, news stories and more to be able to prepare a comprehensive historical contextualization. John tells of Saund’s immigration story, the trajectory of his political career and the importance of the speech, as well as a number of personal details about Saund’s life. His research is currently being peer-reviewed before publication on the RDA website.
John’s research mentor Shawn Parry-Giles, professor and chair in the Department of Communication and co-editor of the RDA project, said the three students working on the RDA project “showed great tenacity in deepening their archival research skills.” The two other students focused on speeches delivered by women's rights activist Emma Guffey Miller promoting the Equal Rights Amendment and by American Indian activist Ruth Muskrat Bronson opposing fishing and timber industries exploiting indigenous land in Alaska.
The students “recovered speeches by people who advanced civil rights for all Americans,” Parry-Giles said. “Most importantly, they experienced the excitement that can come from researching topics they care deeply about.”
Funded by the Mellon Foundation, the open-access site Enslaved.org is led by faculty at UMD, Michigan State University and the University of California, Riverside. It links data collections drawn from multiple universities, archives, museums and family history centers to reconstruct stories and biographies of the lives of the enslaved and their families and communities.
The seven undergraduates who worked on the project this summer developed a dataset of a "slaves for hire" list belonging to the estate of Thomas Cramphin, a wealthy Maryland planter, judge and relative by marriage to the Calvert family. The document—the original which is on loan at the Riversdale House Museum in Riverdale, Maryland—is a record of 32 enslaved persons believed to have been owned and hired out to other individuals by Cramphin or his estate executors after his death.
Using a wide range of primary and secondary sources, including census documents, ancestry records, newspaper articles, historical maps and images and more, they sought to tell the untold stories of the lives of the enslaved individuals.

Ousmane Diop, a Senegalese first-generation American and rising senior at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County, double majoring in history and political science with a minor in Africana studies, said the SROP experience underscored the importance of uplifting the stories of the enslaved, who are sometimes forgotten or ignored.
“Our goal was to decenter the Cramphins and other enslavers while centering the lives of the enslaved individuals in Maryland,” he said. “History is supposed to be diverse and inclusive.”
A data article outlining the students’ research and methodology has been submitted for peer review and publication in the Journal of Slavery and Data Preservation.
Co-Principal Investigator Kristina Poznan, assistant clinical professor in the Department of History, said the students “worked collaboratively and expanded their skills in historical detective work and in using data and digital tools in the humanities.”
Diop added that the SROP affirmed his desire to continue doing research post-graduation: “As an undergraduate, to have your name out there in the ‘dataverse’ where people can see you was really unique and gave me and my peers a lot of momentum,” he said.
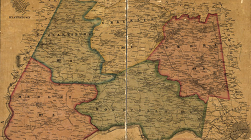
Top image: Martenet and Bond's map of Montgomery County, Maryland [1865]. Learn more.